An ectopic pregnancy is when a foetus develops outside the uterus (womb); it is a rare condition but very serious and should be treated with urgency. Without medical treatment, ectopic pregnancies can become life-threatening; the fallopian tube may rupture, and this can cause infection, severe bleeding, and sometimes death. So, you must understand what an ectopic pregnancy is so you can get help as early as possible.
See also: Does Water and Salt Prevent Pregnancy?
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg doesn’t attach to the uterus during implantation; instead, it attaches to the cervix, fallopian tube or abdominal cavity.
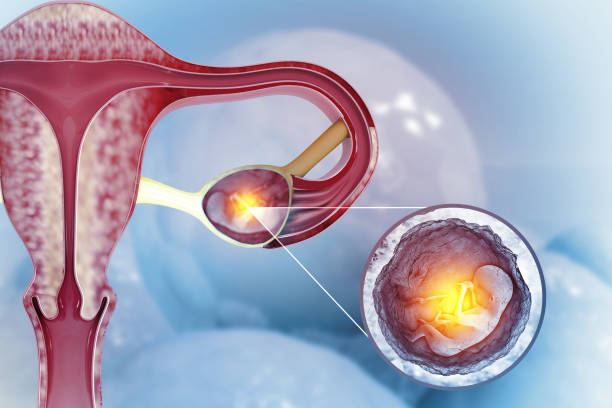
Pregnancy follows a series of steps from fertilisation to delivery; one of these steps is that after fertilisation, the egg travels to the uterus and attaches itself there to start growing the foetus (implantation), but in ectopic pregnancy, the egg attaches itself anywhere outside the uterus.
A pregnancy test may still show that the woman is pregnant, but the foetus can’t properly develop anywhere else aside from the uterus.
What Causes Ectopic Pregnancy
Any woman can experience an ectopic pregnancy without a known cause or risk factor, but that notwithstanding, there are still some possible causes and certain things that can put you at risk of an ectopic pregnancy, including:
- Conception aided by fertility drugs or procedures such as IVF.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Previous ectopic pregnancy.
- Previous surgery on your fallopian tubes.
- Getting pregnant after tubal ligation or while using contraception such as IUD.
- Smoking.
- Age (the risk is higher for women aged 35 to 40).
- Structural abnormalities in the fallopian tube make it hard for the egg to travel to the uterus.
- History of multiple abortions, pelvic surgery, or any abdominal surgery.
- History of STDs such as chlamydia or gonorrhea..
- History of endometriosis.
See also: Pregnancy Test At Home – A Practical Guide
What are the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy usually appears like a normal pregnancy in the beginning, so the symptoms may seem like a reproductive health problem or a miscarriage; that is why regular medical checkup is vital during pregnancy.

Here are some symptoms you may notice for ectopic pregnancy.
- The usual signs of pregnancy (missed period, breast enlargement and tenderness, morning sickness and so on).
- Cramps on one side of the pelvis.
- Pains in the lower abdomen.
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting.
- Pains in the lower back.
- Severe pains that occur on one side of the abdomen.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Rectal pressure.
- Sharp waves of pain in the pelvis, abdomen, neck or shoulder.
- Sudden and severe pain in the lower abdomen (a sign of a ruptured fallopian tube).
How is Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed
After considering the symptoms, if you think you may have an ectopic pregnancy, then you need to see a doctor immediately. However, it can’t be diagnosed by a physical examination, but your doctor will first perform one to rule out other factors that may be causing your symptoms.
The next step is to do a transvaginal ultrasound by inserting a wand into your vagina to see if the gestational sac is in the uterus. A quantitative blood test will also be done to determine your HCG and progesterone levels. These hormones increase drastically during pregnancy, but if they start to decrease or remain the same over a few days and the gestational sac is not in the uterus during the ultrasound, then it can be concluded that the pregnancy is likely ectopic.
How is Ectopic Pregnancy Treated
If you have severe symptoms such as pain and bleeding, there may not even be enough time to carry out all the diagnostic procedures because the fallopian tube may have ruptured already, so emergency surgery would be performed immediately to evaluate the pregnancy. This surgery is known as laparoscopy; it is done to remove the embryo and also attempt to repair the ruptured fallopian tube. During this emergency surgery, a blood transfusion may also be required.
For non-emergency treatment, medication is often used to stop the pregnancy from growing until it slowly disappears; women who undergo this type of treatment will need close monitoring and may need to stay in the hospital for a few days. You will also need to visit the hospital at least once a week to check your HCG levels and confirm if the pregnancy has completely disappeared.
Sometimes, if this treatment is not successful, surgery will still be required to remove the embryo.
See also: Can Ampiclox Prevent Pregnancy?
Can I Get Pregnant Again After Ectopic Pregnancy?
For many women, an ectopic pregnancy happens just once and does not happen again, but for some, it may be reoccurring. If you have only one fallopian tube instead of two, then your chances of getting pregnant again will be low.
So, it is very much possible to get pregnant again after an ectopic pregnancy. If you do get pregnant again, your doctor will do an ultrasound at 6 to 8 weeks to confirm if the baby is developing in the womb (uterus); if it is not, it means it is, unfortunately, another ectopic pregnancy.

Before you attempt to get pregnant again, talk to your doctor or gynaecologist to see if it is safe for you and to guide you to reduce your risks of ectopic pregnancies.
Likewise, if you do not want to get pregnant again, also talk to your healthcare provider to decide on the best contraception method for you.
See also: How To Relieve Back Pain During Pregnancy While Sleeping
Pregnancy loss can be devastating no matter how early it is, coupled with the severe pain that comes with ectopic pregnancies, so one important thing to do after experiencing an ectopic pregnancy is to get all the support and care you need; you can join a support group or be around family and friends. You also need adequate rest, a healthy diet, and mild exercise like walking. Lastly, give yourself time to grieve, and when you are ready, talk to your doctor about ways to ensure healthy pregnancies in future.



