Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints. Unlike the wear-and-tear damage of osteoarthritis, RA affects the lining of your joints, causing a painful swelling that can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity. It is an autoimmune disease, meaning the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. We are going to talk about How To Test For Rheumatoid Arthritis and its treatments.
Importance Of Early Diagnosis Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis affects your immune system. Ignorance of diagnosis and treatment in time could damage your joints. Most people with RA do have some form of joint damage. Most of it happens in the first 2 years. To help confirm a diagnosis, your regular physician might prescribe X-rays and blood tests. Alternatively, you can be assigned someone with Rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and treatment expertise. We call this kind of doctor a rheumatologist.
Early Rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and treatment are absolutely vital. They enhance long-term results and greatly lower the chance of joint injury. Early treatment can help to control symptoms, stop joint and organ deterioration, lower long-term consequences, and enhance quality of life.
Prevalence And Impact On Life
About 1% of the world’s population suffers from Rheumatoid arthritis; women are more often diagnosed than males. Although the disorder can start at any age, it is most usually found between the ages of 30 and 60. Affecting physical, emotional, and social well-being, Rheumatoid arthritis can profoundly influence everyday activities and general quality of life.
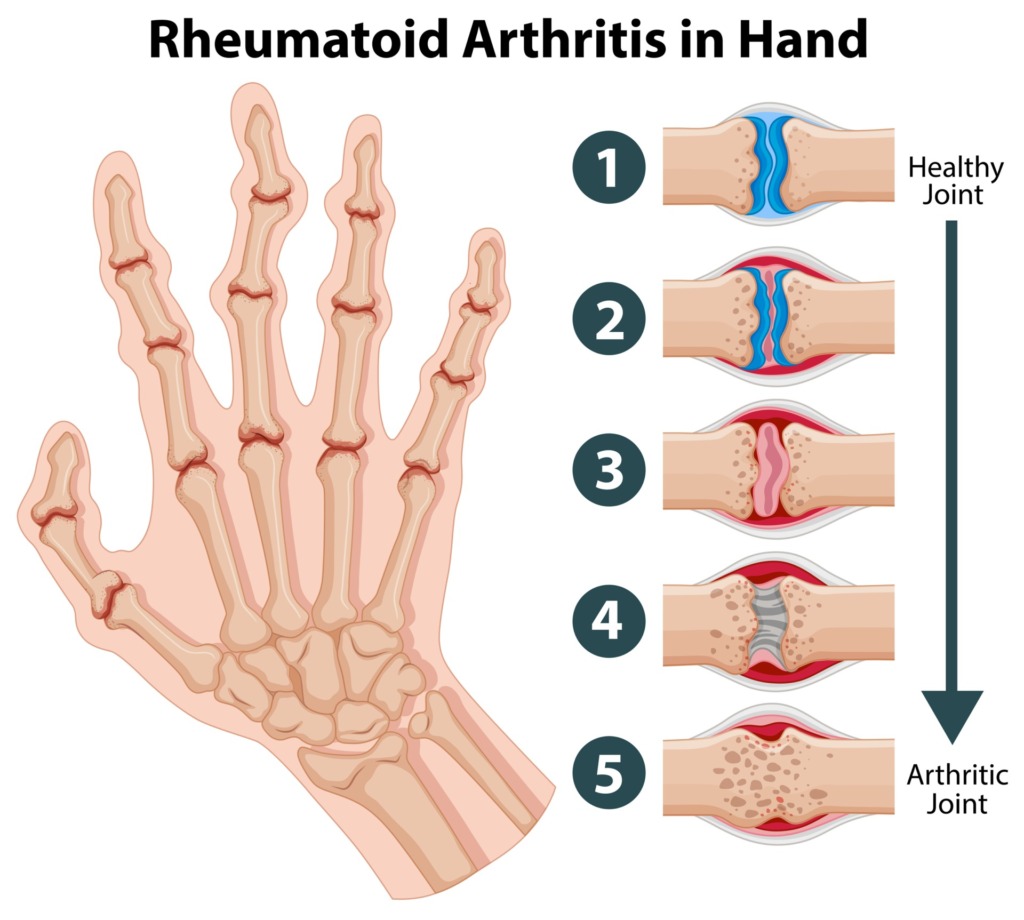
Types Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis
Patients diagnosed with seropositive RA either test positive for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides (anti-CCP) or rheumatoid factor (RF). Usually seen in the blood, these autoantibodies correlate with more severe disease development.
Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
Seronegative RA patients neither exhibit RF nor anti-CCP antibodies in their blood. Even though these markers aren’t present, they can still have serious symptoms and need thorough treatment plans.
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Juvenile RA, sometimes referred to as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, strikes children less than sixteen years old. It includes a number of different kinds of arthritis, all of which cause the joints to become inflamed over time.
Symptoms And Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
- Joint pain and swelling
- Symmetrical pattern of affected joints
Common Symptoms
- Tender, warm, swollen joints
- Joint stiffness that is usually worse in the mornings and after inactivity
- Fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite
Uncommon Symptoms
- Rheumatoid nodules
- Eye inflammation
- Lung involvement
- Blood vessel inflammation
Causes And Risk Factors Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Genetic Factors: RA is largely influenced by genetic inclination. A number of genes, including HLA-DR4, have been linked to a higher chance of the disorder.
Environmental Factors: In those who are genetically predisposed, environmental stressors including smoking, silica dust exposure, and infections can help RA start.
Lifestyle Factors: Choices in lifestyle like smoking and obesity might aggravate RA symptoms and course of development. Two very important preventive actions are keeping a good weight and avoiding smoking.
How To Test For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Blood testing: Those with rheumatoid arthritis often have a raised C-reactive protein (CRP) level or an elevated E-erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), which would suggest an inflammatory activity in the body. Rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies are two other common things that are looked for in blood.
Imaging scans: X-rays could be advised by your doctor to enable monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis development in your joints over time. Your doctor can determine the degree of your ailment in your body by means of MRI and ultrasonic examinations.
Treatment Options
If you find out you have rheumatoid arthritis, don’t freak out. Although there is no treatment, people are living better currently with RA than they have ever done. Your doctor will discuss all the several approaches you could use to manage your symptoms and treat the condition.
Medicines: NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying drugs are some of the different types.
Lower the stress on your joints: Reduce the strain on your joints by either losing or maintaining a reasonable weight. Rest, but not too much; a little exercise also helps. Walkers and canes help you relieve lower body pressure.
Surgery: If over time you have significant joint degeneration, you might have to discuss surgery with your doctor. One can benefit from total joint replacements of the knee, hip, wrist, and elbow. Less major procedures could also be wise choices.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help maintain joint flexibility and strength. Therapists design exercise programs tailored to individual needs to improve mobility and reduce pain.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can significantly impact the management of RA. Smoking cessation is particularly important.
Preventive Measures
Genetic Counseling: For individuals with a family history of RA, genetic counseling can provide insights into the risk and help in early detection.
Environmental Precautions: Avoiding exposure to environmental risk factors like smoking and harmful chemicals can reduce the risk of developing RA.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a nutritious diet and regular physical activity, can help prevent the onset and progression of RA.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis can’t be proven with just one test. Still, several blood tests can point to rheumatoid arthritis as the accurate diagnosis.
Commonly associated with rheumatoid arthritis, blood tests search for inflammation and immune system components. These tests can be combined with scans(x-rays) and a symptom evaluation to identify rheumatoid arthritis.



