In a critical development, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has issued an urgent advisory to healthcare professionals and the public alike, urging heightened awareness regarding a more infectious strain of the virus causing monkeypox (mpox). This highly contagious Clade I monkeypox virus is currently spreading in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), raising concerns about potential global ramifications.
The CDC’s Travel Health Notice underscores the severity of the situation, advising individuals traveling to DRC to minimize contact with the ill, avoid interactions with wild animals, and abstain from consuming or preparing wild game. The Clade I monkeypox strain has been identified as more contagious and capable of causing more severe infections than the Clade II strain, which was linked to the global outbreak observed in 2022-23, primarily affecting gay and bisexual men and other men who have sex with men.
A clade, in the context of monkeypox, represents a broad grouping of viruses that has evolved over decades, forming a genetically and clinically distinct group. Monkeypox itself is characterized by two distinct genetic clades, each posing unique challenges to healthcare systems and public health efforts.
While there have been no reported cases of Clade I in the United States, the CDC emphasizes that the strain is being transmitted through sexually associated human-to-human contact in DRC. This mode of transmission adds a layer of complexity to containment efforts and necessitates a heightened state of alert among healthcare professionals.
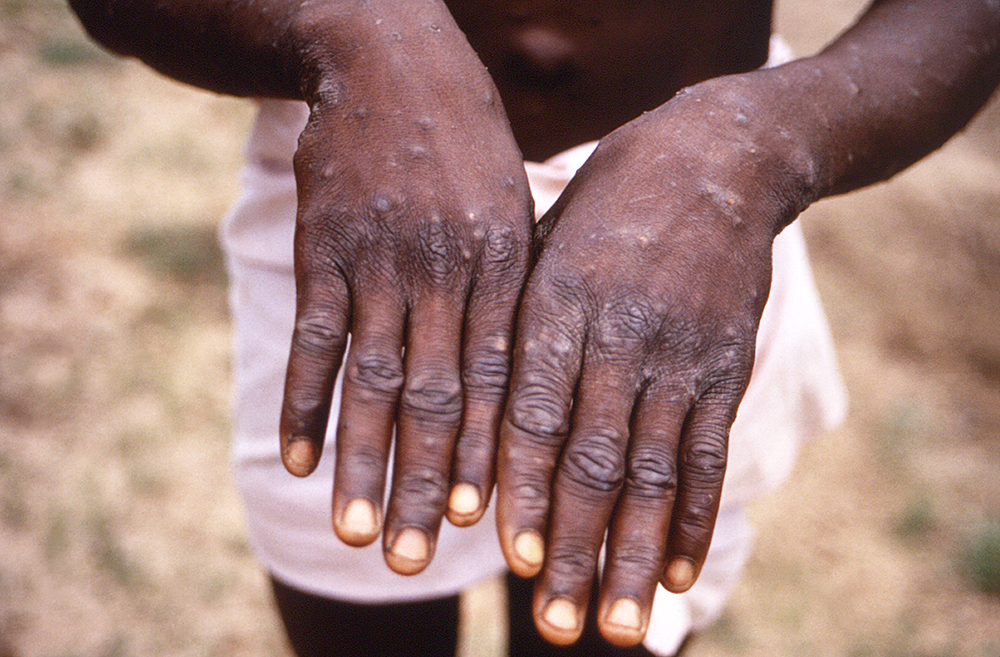
The CDC’s advisory extends beyond basic precautions, emphasizing the importance of considering monkeypox when evaluating patients presenting with rashes. The clinical manifestations of the infection can vary significantly, with lesions described as small, firm, and rubbery, deep-seated, and well-circumscribed, or large, featuring a diffuse, centrifugal distribution.
Healthcare professionals are urged to be vigilant and conduct further investigations for monkeypox if a patient exhibits swollen lymph nodes or has a recent travel history to DRC within 21 days of illness onset. This increased focus on early detection is deemed crucial to prevent potential outbreaks and facilitate prompt containment measures.
Public health officials are also being advised to enhance surveillance through rigorous testing should the Clade I strain be detected in the United States. The CDC underscores the importance of expeditiously sending specimens collected from patients who have traveled to DRC for testing to facilitate a swift response.
Since January, DRC has reported a staggering number of clinically diagnosed but not laboratory-confirmed monkeypox cases, exceeding 12,500, with nearly 600 suspected deaths attributed to the virus. This represents a substantial increase compared to the median of 3,767 suspected cases reported annually in DRC during the years 2016-2021, highlighting the urgency of the situation.
In the 2022-23 outbreak, over 31,000 Americans were diagnosed with monkeypox, resulting in 55 deaths, according to CDC data. Despite the availability of a vaccine called Jynneos, vaccination coverage in the US remains low, with only 1 in 4 eligible individuals having received both doses required for full protection.
The CDC, in its advisory, emphasizes that individuals at high risk for monkeypox include gay and bisexual men, other men who have sex with men, transgender and nonbinary individuals with recent sexually transmitted disease diagnoses, those with multiple sex partners, individuals engaged in sexual activities at commercial sex venues or large public events in affected areas, and those planning to participate in such activities.
As the global community grapples with the ongoing challenges posed by infectious diseases, the CDC’s alert serves as a stark reminder of the importance of international collaboration, early detection, and robust public health measures to curb the spread of emerging threats. The situation in DRC underscores the need for continued vigilance and proactive measures to protect public health on a global scale.