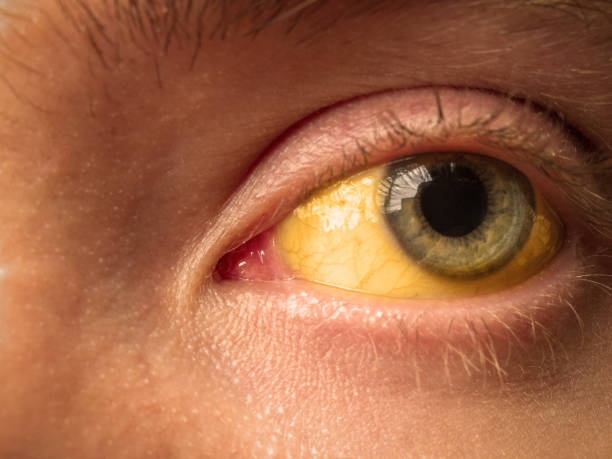
Jaundice is a medical condition characterised by yellowish eyes and skin resulting from the buildup of too much bilirubin in the blood. This is due to the inability of the liver to filter it from the blood into the digestive system for removal.
Bilirubin is produced from the breakdown of haemoglobin (the red pigment in blood that carries oxygen around the body).
Naturally, bilirubin is transported to the liver through the blood and then passes through the bile ducts into the small intestine. Eventually, it is passed out through urine or stool.
Causes
Jaundice can occur from liver damage or any condition that affects liver function. Some common causes include:
- Viral hepatitis: an inflammation of the liver caused by an autoimmune response to alcohol, drugs, or toxins or an infection from any of the hepatitis viruses.
- Liver cirrhosis: scarring of the liver tissue due to liver diseases or long-term infections and exposure to toxic substances.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis: the damage of the bile ducts due to inflammation often instigated when the immune system attacks the cells of the bile ducts.
- Liver cancer: the development and multiplication of cancerous cells in the liver tissues.
- Leptospirosis: a bacterial infection that is often spread by infected animals.
Symptoms of Jaundice
Aside from yellowing of skin and eyes, there are other symptoms you are likely to experience as a result of jaundice; they include:
- Fever.
- Loss of appetite.
- Abnormal weight loss.
- Skin itching.
- Weakness.
- Sudden drowsiness or confusion.
- Throwing up.
- Swelling of your abdomen or legs.
- Darkening skin.
- Feeling sick.
- Blood in stool or vomit.
- Muscles or joint pain.
- Dark urine or pale stool.
- Easy bruising or bleeding.
- Bloody nose.
Treatment
Jaundice usually doesn’t require treatment in adults, but the underlying causes and symptoms can be treated. Once the cause is treated and the liver improves, jaundice will naturally clear out with time. However, jaundice requires treatment in infants because the condition is usually severe for infants. So here are the treatment options for jaundice in infants.
- Phototherapy: The baby is undressed and put under a special light that breaks down bilirubin in the skin so it can be excreted.
- Additional feeding: More frequent feeding and some supplements may be recommended.
- Blood protein transfusion: An IV transfusion of immunoglobulin (IVIg) may be required if the jaundice is related to blood type incompatibility with the mother.
- Exchange transfusion of blood: Small amounts of the baby’s blood are withdrawn repeatedly and replaced with a donor’s blood to dilute the antibodies and bilirubin in the baby.