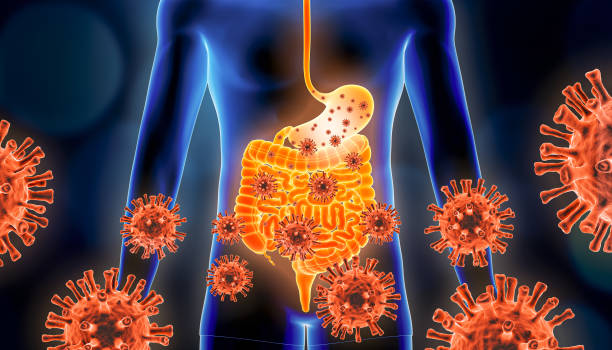
Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines due to an infection; it can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection or reaction to certain chemicals. The first signs are usually abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea.
This inflammation makes the organs feel sore and swollen, but in some cases, they will heal within a few days. However, gastroenteritis causes severe dehydration due to excess fluid loss, so a person suffering from this condition will need a rapid replacement of fluid either orally or intravenously.
For older adults, infants and people with compromised immune systems, this condition can be deadly and should be taken seriously.
Causes
Many things can result in gastroenteritis, including:
- Bacteria such as the Campylobacter bacterium.
- Viruses such as calicivirus, norovirus, rotavirus, adenovirus and astrovirus.
- Parasites such as Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica, and Cryptosporidium.
- Medication such as antibiotics can cause gastroenteritis in susceptible people.
- Chemicals such as lead can trigger gastroenteritis.
- Bacterial toxins: These are the poisonous by-products of bacteria that contaminate food and water. Some strains of staphylococcal bacteria can cause gastroenteritis by producing harmful toxins.
Symptoms of Gastroenteritis
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
- Abdominal pain.
- Loss of appetite.
- Fever.
- Bodyaches.
- Fatigue.
- Chills.
Gastroenteritis usually begin suddenly, and you will notice symptoms involving your stomach and intestines; then, it can become serious, and you will start noticing systemic symptoms such as fever. When it becomes severe, you will see signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth, dry skin, excessive thirst, sunken eyes, little to no urination, muscle weakness, blurred vision and lightheadedness. Take plenty of fluids and get immediate medical attention when you start noticing dehydration.
Treatment
You may not need treatment for this condition; it will go away after a few days if it is not severe, but you must stay hydrated. However, treatment options still depend on the cause; they include:
- Plenty of fluids.
- Intravenous fluid replacement.
- Oral rehydration drinks.
- Antibiotics, if it is caused by bacteria.
- Antiparasitic drugs if it is caused by parasites.
- Do not take anti-diarrhoea or anti-vomiting medications unless a doctor prescribes them because your body is getting rid of the infection through vomiting and diarrhoea.