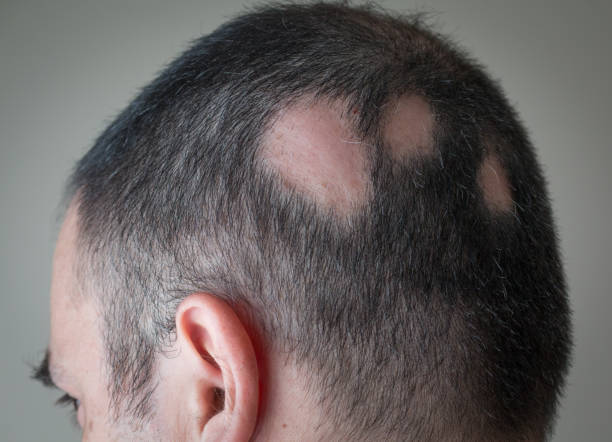
Alopecia is an autoimmune disorder that results in unpredictable hair loss due to the immune system attacking hair follicles. If there is total hair loss in the scalp, it is called alopecia totalis; if there is hair loss in small patches, it is alopecia areata, but if there is hair loss throughout the body, then it is referred to as alopecia universalis. Alopecia can also cause hair thinning, called diffuse alopecia areata.
This condition can affect anybody regardless of age, gender, or race, but it is more common in men. It can also be permanent or temporary.
Alopecia is usually caused by hormonal changes, genetics, ageing or medical conditions. The cause of alopecia will determine its treatment because it can be a normal part of ageing, and alopecia is not life-threatening or painful. Still, it may have some psychological effects on a person.
Causes
Alopecia occurs when the immune system or white blood cells attack hair follicles and cause them to shrink; it slows down hair production and causes hair to fall off. However, there is no known cause of alopecia. Still, experts have suggested genetics, medications, hormonal changes, radiation therapy, ageing, stress, and some medical conditions like high fever, infection, anaemia, tumour, blood loss, crash diet and so on.
Symptoms of Alopecia
The common symptoms of alopecia include:
- Nail pitting.
- Acne, facial hair, or an abnormal menstrual cycle.
- Circular or patchy bald spots.
- Complete body hair loss.
- Sudden loosening of the hair.
- Scaling or patches that spread over the scalp.
- White hair.
- Gradual thinning of the scalp hair.
- Hair loss on the beard.
- Loss of eyelashes.
- Loss of eyebrows.
- Band of hair loss.
- Brittle and crumbling nails.
Treatment
Hair can regrow by itself in some cases of alopecia, but there are effective treatment methods that you can use to grow your hair or slow down hair loss.
Medication
If an underlying medical condition causes the alopecia, a doctor will diagnose and treat it first. Medications treat hereditary alopecia; the most common options include minoxidil, finasteride, and other oral medicines like dutasteride (Avodart) and spironolactone (Carospir, Aldactone).
Hair Transplant Surgery
If the hair loss only affects the scalp, the most effective treatment is hair transplant or restoration surgery. During this surgery, a dermatologist removes the hair from the area that still has hair and transplants it to the bald spots; this way, they can spread the hair throughout the scalp.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy has been approved for treating hereditary hair loss in both men and women. It involves the use of a low-level laser device, and studies have shown it can improve hair density.