For many families, the decision to formula-feed their babies is a complex and deeply personal one. Although the formula is vital for healthy development, concerns arise about its potential association with the serious intestinal condition Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC).
This condition is a devastating gastrointestinal illness that primarily affects premature infants. While its exact cause remains unclear, several factors contribute to its development, including prematurity, feeding practices, and gut health. Recent research explores a baby formula-NEC link, sparking concern among healthcare professionals and parents and fostering debate and scrutiny.
In this article, we will explore the latest scientific evidence surrounding the potential link between infant formula and NEC.
Understanding Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
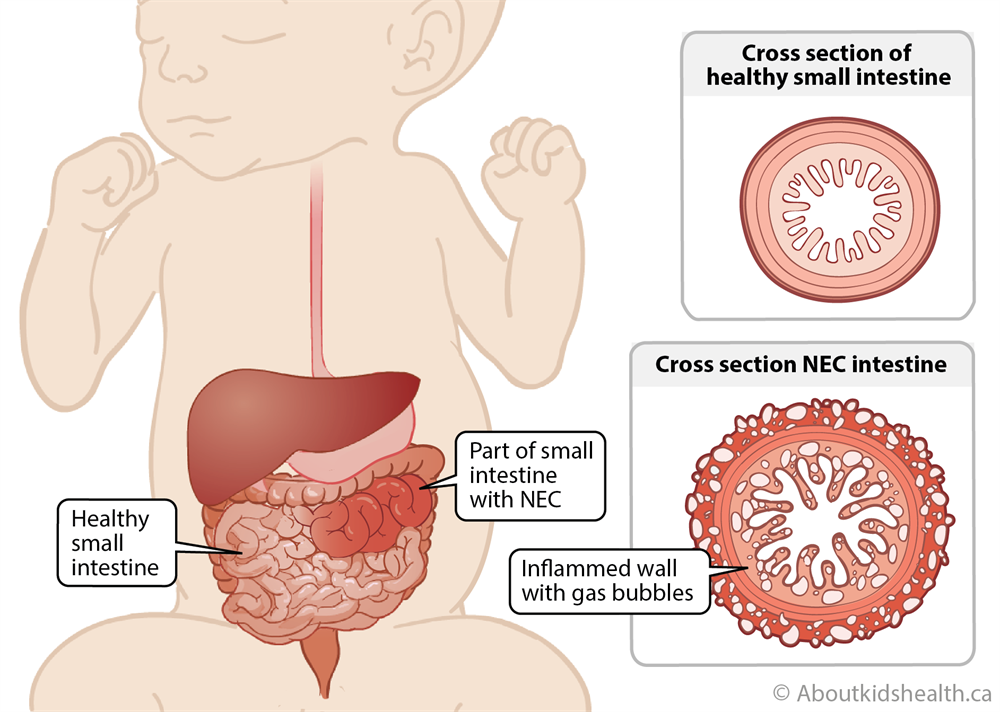
NEC is a severe gastrointestinal condition predominantly impacting premature infants. It arises when the intestinal lining becomes inflamed and undergoes necrosis, posing the risk of a life-threatening perforation in the intestine. This condition commonly manifests within the baby’s second to third week of life.
According to a National Institute of Health study, these global incidences occur in 0.3 to 2.4 infants for every 1000 births. Nearly 70% of cases occur in premature babies born before 36 weeks, impacting 2% to 5% of them. The condition is responsible for nearly 8% of NICU admissions, and mortality ranges from 10% to 50%. The data underscores the severity of his condition.
TorHoerman Law mentions symptoms of NEC can include abdominal distention, fluctuations in pulse and arterial pressure, vomiting, bloody stools, and lethargy. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial to improve outcomes, which can range from complete recovery to bowel resection and long-term complications. Understanding the causes and risk factors for this condition is essential for optimizing care and preventing this devastating condition in vulnerable infants.
Components of Baby Formula
Typically, commercial infant formulas encompass a blend of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, with variations tailored to meet specific dietary needs. However, they differ significantly in their specific components, some of which may contribute to the risk of this condition.
The key ingredients in infant formula play a crucial role in infant nutrition, with potential implications for NEC development. Cow’s milk protein, particularly casein, may contribute to gut inflammation. The types and ratios of fats derived from vegetable oils can vary, impacting premature infants’ gut health.
Lactose, the primary carbohydrate, may pose digestion challenges for some infants. Fortified with essential vitamins and minerals, imbalances, especially in iron, could potentially increase the risk. Also, prebiotics and probiotics in some formulas show promise in promoting gut health, although further research is needed for conclusive evidence.
As we probe the potential link between baby formula and this condition, an in-depth examination of these components becomes essential.
Scientific Studies and Research
Retrospective studies analyzing cases of this health risk have provided valuable insights. Studies suggest premature infants fed specific formulas have a higher NEC incidence compared to those exclusively receiving breast milk.
Drugwatcher reported that premature babies given cow’s milk-based formula maybe ten times more likely to develop the condition. Infants supplementing human milk with cow milk formula are three times more likely to develop the risk.
These findings underscore the potential risks associated with cow’s milk-based formula for premature infants. Current research is exploring the role of oligosaccharides, bioactive compounds found in breast milk, in mitigating NEC risk.
Factors Influencing NEC
Exploring factors contributing to NEC onset involves navigating a complex terrain, emphasizing the intersection with infant formula use. This exploration focuses on understanding multifaceted elements influencing this development and their potential link with baby food.
Premature birth, a primary risk, exposes infants to an underdeveloped gastrointestinal tract susceptible to inflammation. The compromised immune system amplifies the risk in premature infants, emphasizing the delicate immune balance. Formula feeding, while not a sole cause, is scrutinized for potential inflammatory triggers affecting the development of immature guts.
Dissecting the condition reveals a complex interplay of prematurity, immune function, and nutritional choices. Personalized care for preterm infants is essential to mitigate the risk of this devastating condition.
Controversies and Conflicting Perspectives
Key controversies surrounding the link between formula and NEC include challenges in establishing causality due to observational studies. Wide variations in formula composition and feeding practices complicate drawing universal conclusions.
The debate centers on specific ingredients like cow’s milk protein, prebiotics, and probiotics. Concerns about industry influence on research funding raise questions about potential bias.
Conflicting perspectives on formula and NEC exist among healthcare professionals, with some advocating exclusive breastfeeding for premature infants. The Journal of the American Heart Association suggested that a higher dose or longer duration of human milk or breastfeeding reduces NEC incidence. Formula industry representatives assert safety and nutrition, emphasizing personalized approaches.
Parents navigate conflicting information, experiencing emotional challenges and confusion in infant feeding choices.
As controversies persist, acknowledging the multifaceted nature of this condition and the intricate interplay between various elements remains paramount.
Considerations for Parents and Caregivers
Parents and caregivers, in navigating infant nutrition and the potential formula-NEC link, grapple at the intersection of research, healthcare decisions, and legal considerations. They must be well-informed and proactive in addressing various aspects related to their infant’s well-being.
Consider consulting healthcare professionals for personalized guidance on feeding practices and formula selection based on individual risk factors. Breast milk, if feasible, offers ideal nutrition and reduces the risk. Explore formulas with prebiotics, probiotics, or hydrolyzed protein for potential benefits. Monitor feeding practices, use slow-flow nipples, and be vigilant for NEC symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention if necessary.
Consumer notice reports baby formula lawsuits filed against Abbott Laboratories and Mead Johnson for NEC development in premature babies. In August 2022, judges consolidated these lawsuits into an Illinois multidistrict litigation due to the nationwide scope. As of Dec. 15, 2022, there were 88 pending cases, underscoring the legal significance and widespread concern surrounding these allegations.
Recent years have seen an emergence of legal actions related to NEC and baby food. Many parents have pursued legal avenues, filing lawsuits against formula manufacturers, alleging that specific formulations contributed to the condition in their infants. The NEC baby formula lawsuit signifies parents’ pursuit of accountability and restitution in ongoing legal proceedings against formula manufacturers.
Regulatory Measures and Industry Practices
Regulatory bodies like the FDA enforce stringent standards for infant formula safety, ensuring adherence to nutritional requirements and rigorous testing. Formula manufacturers prioritize robust quality control, continuously monitoring production processes and ingredient sourcing.
The newborn food industry prioritizes research and innovation, refining compositions, incorporating bioactive components, and enhancing safety to address NEC concerns.
Recent industry trends show a growing emphasis on incorporating prebiotics, probiotics, and human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) into formulas. These components, inspired by breast milk, are believed to confer health benefits and may contribute to reducing the health risk.
Untying the Complexity
Exploring the baby formula-NEC link reveals a complex landscape where scientific research, controversies, and parental considerations converge and intertwine. The intricate interplay of factors, including prematurity, immune function, and formula composition, underscores the complexity of NEC’s origins.
Continuing the quest for knowledge highlights the necessity of a collaborative effort to address the potential baby formula-NEC link. Uniting healthcare professionals, researchers, regulatory bodies, and caregivers is crucial for a holistic understanding of the health condition. This collaborative approach guides the path toward safer and more effective infant feeding practices.



